Carbohydrates can be designated with a variety of special terms that you need to be familiar with.
Pentose – a carbohydrate
with five carbon atoms
Hexose – a carbohydrate
with six carbon atoms
Aldose – a carbohydrate
that has an aldehyde carbonyl group
Ketose – a carbohydrate
that has a ketone carbonyl group
Pyranose – a six-membered
ring form of a carbohydrate
Furanose – a five-membered
ring form of a carbohydrate
D-Carbohydrate – the
stereocenter farthest from the carbonyl group is the same as is found
in D-glyceraldehyde (-OH group is to the right on a Fischer projection)
L-Carbohydrate – the
stereocenter farthest from the carbonyl group is the same as is found
in L-glyceraldehyde (-OH group is to the left on a Fischer projection)
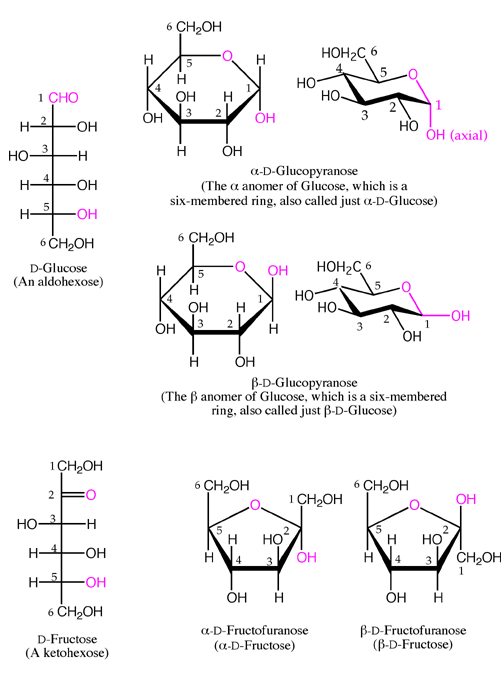
Alpha – the –OH
group on the anomeric carbon is on the opposite side of the ring as the
terminal –CH2OH group. For glucose in the
ring (pyranose) form this is axial.
Beta - the –OH group
on the anomeric carbon is on the same side of the ring as the terminal
–CH2OH group. For glucose in the ring form
(pyranose) this is equatorial.
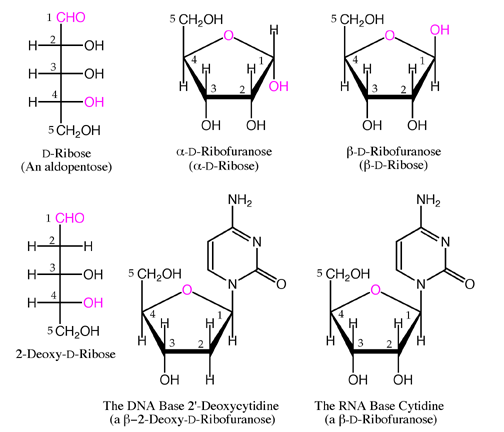
Five-membered rings are the most stable form of some carbohydrates. For example D-fructose, a ketohexose, forms a stable five-membered ring. Ribose, a common aldopentose, also forms a five-membered ring. Ribose is important in biochemistry because it is the “sugar” part of the RNA bases such as cytidine. Some sugars are missing –OH groups, and these are indicated by the number corresponding to the location of the missing –OH group, followed by the term “deoxy” meaning “without oxygen”. 2-Deoxy-D-ribose is the “sugar” on DNA bases, for example the base 2’-deoxycytidine.