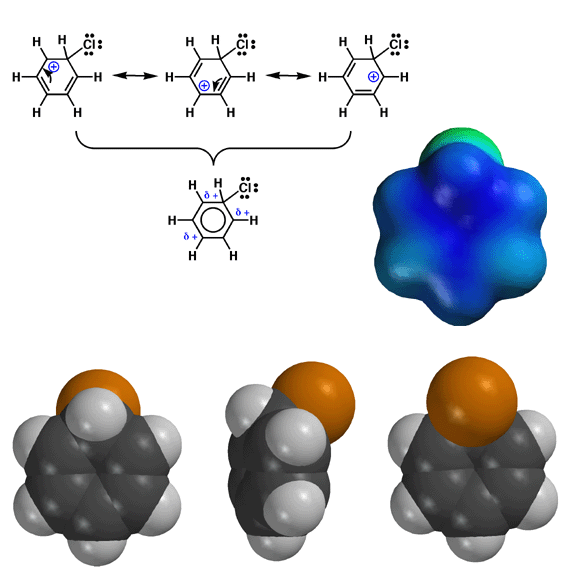
|
|
Shown
above are models of the arenium ion produced during the chlorination of benzene. The
chlorine atom is brown. As described by the electrostatic potential energy
surface on the right, the positive charge (blue color) of the arenium ion
is localized at the positions ortho and para to where the electrophile is
attached. You should be able to draw resonance forms that predict the ortho
and para distribution of the positive charge. This ortho and para distribution
of positive charge is important because substituents already on an aromatic
ring must interact with this charge distribution, and the result of that
interaction is a modulation of rate and orientation of reaction. By understanding
these interactions, you will be able to predict accurately the products of
electrophilic substitution reactions that take place on aromatic rings containing
substituents. |